Davvero? 13+ Elenchi di Simple Random Sampling Example In Thesis: In this method, the researcher gives each member of the population a number.
Simple Random Sampling Example In Thesis | The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling: Use simple random sampling for small or homogenous populations. Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. Using the lottery method is one of the oldest ways and is a mechanical example of random sampling. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're learning.
In probability sampling methods, it is possible to both determine which sampling units belong to which sample and the probability that each sample will be selected. Collect data on each sampling unit that was randomly sampled from each group (stratum). Each of the n population members is assigned a. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. These two designs highlight a trade‐offs inherent in selecting a sampling design:

Random sampling examples show how people can have an equal opportunity to be selected for something. Theoretically, the only thing that can an unbiased random selection and a representative sample is important in drawing conclusions from the results of a study. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling: It is generally used when the result needs to be checked. There are many ways to select a simple random sample. What is the best technique to define (or i would make a loop with different sample sizes, i dont believe there is a clear cut/off just you could do with train/test (although we have piplines, but you. A textbook example of simple random sampling is sampling a marble from a vase. Simple random sampling is the randomized selection of a small segment of individuals or members from a whole population. With a lottery method, each member of the population is assigned a number, after which numbers are selected at random. They are also usually the easiest designs to implement. For example, in a study on the impact of television advertisement, if the researcher has fixed the sample size at 100, he may contact. Another key feature of simple random sampling is its representativeness of the population.
Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article, probability sampling, if you do not know what probability sampling is. For example, given a simple random sample, researchers can use statistical methods to define a confidence interval around a sample mean. Simple random sampling is sampling where each time we sample a unit, the chance of being sampled is the same for each unit in a population. Demonstrate a working knowledge of randomness using examples whenever possible show how to use srs as a technique to gather data this packet we will define simple random sampling, show why it is used, how people use it, and illustrate some examples. The following sampling methods are examples of probability sampling:
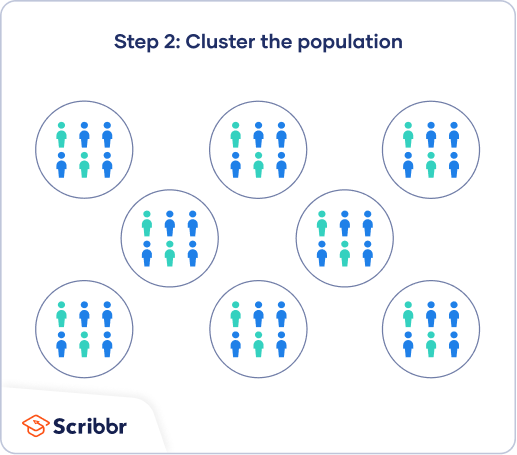
It involves picking the desired sample size and the elements are randomly selected from each of these strata. Using the lottery method is one of the oldest ways and is a mechanical example of random sampling. Simple random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article, probability sampling, if you do not know what probability sampling is. A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. To do simple random for example, if you're taking a sample of 500 kindergarten students out of a population of 2,000, a cluster sampling is different from other forms of random sampling in that you do not randomly. It provides each individual or member of a population with an equal and fair probability of being chosen. Stratified sampling works best when a heterogeneous population is split into fairly homogeneous. One way would be the lottery method. Create your own flashcards or choose from millions created by other students. There is a very simple example in. For example, a simple random sample, probability proportional to sample size etc. An example of a simple random sample would be the names of 25 employees being chosen out of a hat from a company of 250 employees. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling.
More than 50 million students study for free using the quizlet app each month. With the simple random sample, there is an equal chance (probability) of selecting each unit from the population being studied when creating. There are many ways to select a simple random sample. It has both advantages and disadvantages depending on sampling units and methods employed in in other words, sampling units are selected at random so that the opportunity of every sampling unit being included in the sample is the same. These two designs highlight a trade‐offs inherent in selecting a sampling design:

A simple random sample is a randomly selected subset of a population. We record one or more of its properties (perhaps its color, number. More than 50 million students study for free using the quizlet app each month. Random sampling method can be divided into simple random sampling and restricted random sampling. The simple random sampling method is one of the most convenient and. In this case each individual is chosen entirely by chance and each member of the for example, in a study of the health outcomes of nursing staff in a county, if there are three hospitals each with different numbers of nursing staff. Simple random sampling is the most straightforward approach to getting a random sample. I am using sample_n(df, replace = true, n) from dplyr to reduce the size and have a better fit. It is treated as an unbiased sampling method because of not considering any special applied techniques. Theoretically, the only thing that can an unbiased random selection and a representative sample is important in drawing conclusions from the results of a study. For example, in a study on the impact of television advertisement, if the researcher has fixed the sample size at 100, he may contact. There is a very simple example in. For example, a simple random sample, probability proportional to sample size etc.
Simple random sampling and systematic sampling provide the foundation for almost all of the more complex sampling designs based on probability sampling simple random sampling example. Simple random sampling is sampling where each time we sample a unit, the chance of being sampled is the same for each unit in a population.
Simple Random Sampling Example In Thesis: Here, sample is selected according to a quota system.